Loading the Kernel (Part 2)
In the previous section, we located the kernel image and determined its size. In this section, we'll continue with our plan. We'll allocate memory for the kernel image, read it into memory, exit the Boot Services, and jump to the kernel image.
Allocate memory
We'll use the Boot Services AllocatePages function to allocate enough pages, starting at address 0x100000 (1 MiB), to hold the kernel image. We'll also allocate a region of memory for the kernel stack. Let's define the AllocatePages function, which also requires defining the EfiAllocateType and EfiPhysicalAddress types.
# src/common/uefi.nim
type
EfiBootServices* = object
...
allocatePages*: proc (
allocateType: EfiAllocateType,
memoryType: EfiMemoryType,
pages: uint,
memory: ptr EfiPhysicalAddress
): EfiStatus {.cdecl.}
...
EfiAllocateType* = enum
AllocateAnyPages,
AllocateMaxAddress,
AllocateAddress,
MaxAllocateType
EfiPhysicalAddress* = uint64
The EfiAllocateType enum is used to specify the type of allocation. We'll use AllocateAddress to allocate pages for the kernel image, starting at a specific address (in our case, 0x100000). The EfiMemoryType enum is used to specify the type of memory to allocate, which we'll set to OsvKernelCode. For the kernel stack, we'll use AllocateAnyPages to allocate any pages, and set the memory type to OsvKernelStack.
# src/boot/bootx64.nim
const
PageSize = 4096
KernelPhysicalBase = 0x100000
KernelStackSize = 128 * 1024'u64
proc EfiMainInner(imgHandle: EfiHandle, sysTable: ptr EFiSystemTable): EfiStatus =
...
consoleOut &"boot: Allocating memory for kernel image "
let kernelImageBase = cast[pointer](KernelPhysicalBase)
let kernelImagePages = (kernelInfo.fileSize + 0xFFF).uint div PageSize.uint # round up to nearest page
checkStatus uefi.sysTable.bootServices.allocatePages(
AllocateAddress,
OsvKernelCode,
kernelImagePages,
cast[ptr EfiPhysicalAddress](addr kernelImageBase)
)
consoleOut &"boot: Allocating memory for kernel stack (16 KiB) "
var kernelStackBase: uint64
let kernelStackPages = KernelStackSize div PageSize
checkStatus uefi.sysTable.bootServices.allocatePages(
AllocateAnyPages,
OsvKernelStack,
kernelStackPages,
kernelStackBase.addr,
)
Read kernel image
The next step is to use the read function of the EfiFileProtocol to read the kernel image into memory. Let's define the read function.
# src/common/uefi.nim
type
EfiFileProtocol* = object
...
read*: proc (
this: ptr EfiFileProtocol,
bufferSize: ptr uint,
buffer: pointer
): EfiStatus {.cdecl.}
...
We'll use the read function to read the kernel image into the memory we allocated earlier.
# src/boot/bootx64.nim
proc EfiMainInner(imgHandle: EfiHandle, sysTable: ptr EFiSystemTable): EfiStatus =
...
# read the kernel into memory
consoleOut "boot: Reading kernel into memory"
checkStatus kernelFile.read(kernelFile, cast[ptr uint](addr kernelInfo.fileSize), kernelImageBase)
Close open files
We're done with the kernel file and the root directory, so we can close them. It's not strictly needed, but I got in the habit of closing resources when I'm done with them. Let's define the close function of the EfiFileProtocol.
# src/common/uefi.nim
type
EfiFileProtocol* = object
...
close*: proc (this: ptr EfiFileProtocol): EfiStatus {.cdecl.}
...
# src/boot/bootx64.nim
proc EfiMainInner(imgHandle: EfiHandle, sysTable: ptr EFiSystemTable): EfiStatus =
...
# close the kernel file
consoleOut "boot: Closing kernel file"
checkStatus kernelFile.close(kernelFile)
# close the root directory
consoleOut "boot: Closing root directory"
checkStatus rootDir.close(rootDir)
Get memory map
In order to get the memory map, we have to allocate memory for the map itself. But how do we know how much memory to allocate? Calling getMemoryMap with a buffer size of 0 will return the required buffer size in the memoryMapSize output parameter. We can then allocate the required memory and call getMemoryMap again to get the actual memory map.
Let's define the getMemoryMap function first (and the associated EfiMemoryDescriptor and EfiVirtualAddress types). We'll also define the allocatePool function of the EfiBootServices type, which we'll use to allocate the memory for the memory map. (The difference between allocatePages and allocatePool is that allocatePages allocates memory in page-sized chunks, whereas allocatePool allocates memory in byte-sized chunks. allocatePool also provides more control over the address of the allocated memory, which is why we used it to allocate memory for the kernel.)
# src/common/uefi.nim
type
EfiBootServices* = object
...
getMemoryMap*: proc (
memoryMapSize: ptr uint,
memoryMap: ptr EfiMemoryDescriptor,
mapKey: ptr uint,
descriptorSize: ptr uint,
descriptorVersion: ptr uint32
): EfiStatus {.cdecl.}
allocatePool*: proc (
poolType: EfiMemoryType,
size: uint,
buffer: ptr pointer
): EfiStatus {.cdecl.}
...
EfiMemoryDescriptor* = object
`type`*: EfiMemoryType
physicalStart*: EfiPhysicalAddress
virtualStart*: EfiVirtualAddress
numberOfPages*: uint64
attribute*: uint64
...
EfiPhysicalAddress* = uint64
EfiVirtualAddress* = uint64
Now we're ready to get the memory map.
# src/boot/bootx64.nim
proc EfiMainInner(imgHandle: EfiHandle, sysTable: ptr EFiSystemTable): EfiStatus =
...
# memory map
var memoryMapSize = 0.uint
var memoryMap: ptr UncheckedArray[EfiMemoryDescriptor]
var memoryMapKey: uint
var memoryMapDescriptorSize: uint
var memoryMapDescriptorVersion: uint32
# get memory map size
status = uefi.sysTable.bootServices.getMemoryMap(
addr memoryMapSize,
cast[ptr EfiMemoryDescriptor](nil),
cast[ptr uint](nil),
cast[ptr uint](addr memoryMapDescriptorSize),
cast[ptr uint32](nil)
)
# increase memory map size to account for the next call to allocatePool
inc memoryMapSize, memoryMapDescriptorSize
# allocate pool for memory map (this changes the memory map size, hence the previous step)
consoleOut "boot: Allocating pool for memory map"
checkStatus uefi.sysTable.bootServices.allocatePool(
EfiLoaderData, memoryMapSize, cast[ptr pointer](addr memoryMap)
)
# now get the memory map
consoleOut "boot: Getting memory map"
checkStatus uefi.sysTable.bootServices.getMemoryMap(
addr memoryMapSize,
cast[ptr EfiMemoryDescriptor](memoryMap),
addr memoryMapKey,
addr memoryMapDescriptorSize,
addr memoryMapDescriptorVersion
)
Exit boot services
We have all the information we need to exit the Boot Services. Let's define the exitBootServices function.
# src/common/uefi.nim
type
EfiBootServices* = object
...
exitBootServices*: proc (
imageHandle: EfiHandle,
mapKey: uint
): EfiStatus {.cdecl.}
...
The call to exitBootServices requires passing the mapKey that we got from getMemoryMap. This ensures that the memory map hasn't changed since we got it, otherwise the call will fail.
# src/boot/bootx64.nim
proc EfiMainInner(imgHandle: EfiHandle, sysTable: ptr EFiSystemTable): EfiStatus =
...
# exit boot services
consoleOut "boot: Exiting boot services"
checkStatus uefi.sysTable.bootServices.exitBootServices(imgHandle, memoryMapKey)
If we compile and run now, we are faced with the following error:
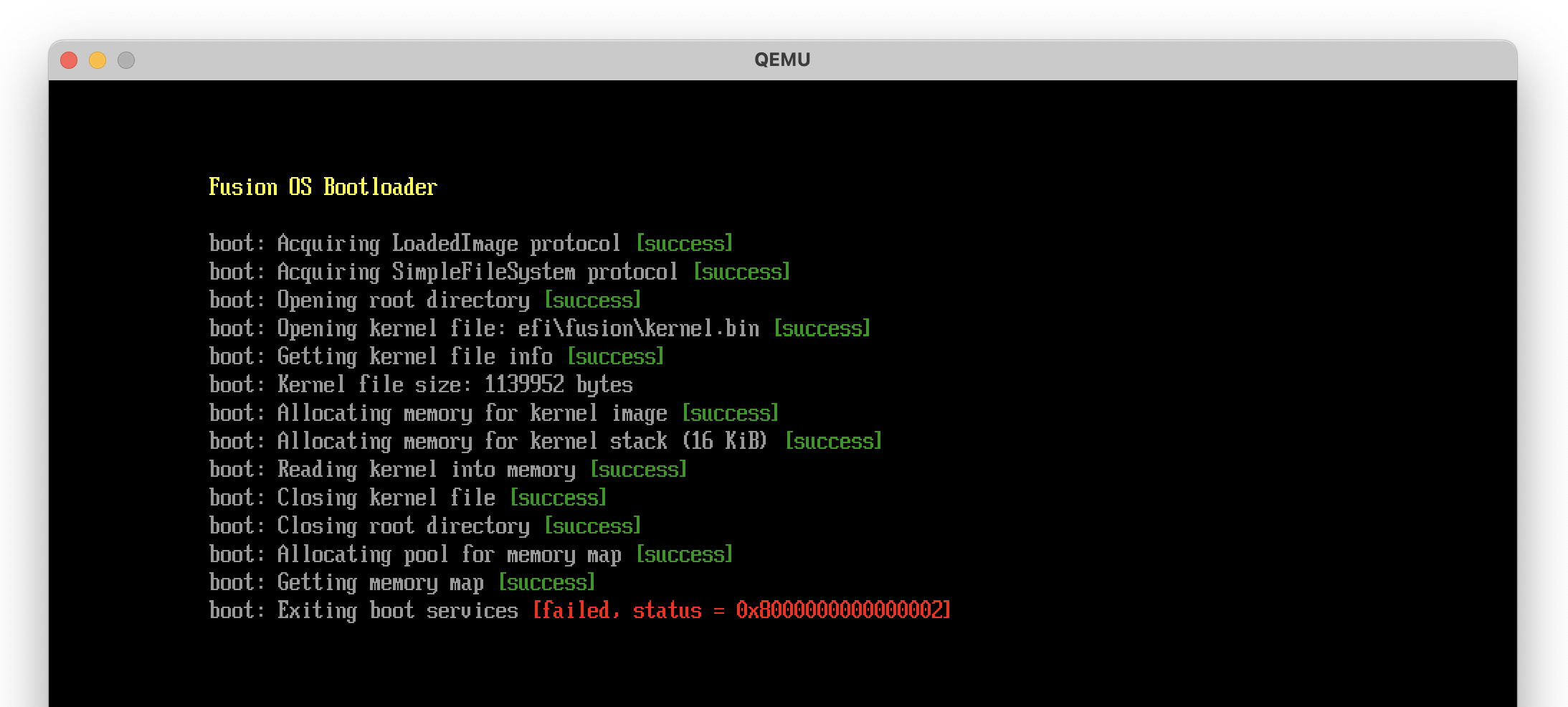
Status code 2 is EfiInvalidParameter, which means that the mapKey we passed to exitBootServices is invalid. How can the mapKey be invalid if we just got it from getMemoryMap? This took me a while to figure out, but it turns out that merely printing to the console (or any other boot service call) may allocate memory, which changes the memory map. So basically we have to call exitBootServices immediately after getting the memory map, without calling any other boot service function in between. So, unfortunately, we'll have to give up printing to the console from that point on, until we transfer control to the kernel.
Let's change the call to checkStatus to avoid printing to the console (we'll only print to the console in case of an error).
# src/boot/bootx64.nim
proc EfiMainInner(imgHandle: EfiHandle, sysTable: ptr EFiSystemTable): EfiStatus =
...
# get memory map
echo "boot: Getting memory map and exiting boot services"
status = uefi.sysTable.bootServices.getMemoryMap(
addr memoryMapSize,
cast[ptr EfiMemoryDescriptor](memoryMap),
addr memoryMapKey,
addr memoryMapDescriptorSize,
addr memoryMapDescriptorVersion
)
# IMPORTANT: After this point we cannot output anything to the console, since doing
# so may allocate memory and change the memory map, invalidating our map key. We can
# only output to the console in case of an error (since we quit anyway).
if status != EfiSuccess:
echo &"boot: Failed to get memory map: {status:#x}"
quit()
status = uefi.sysTable.bootServices.exitBootServices(imgHandle, memoryMapKey)
if status != EfiSuccess:
echo &"boot: Failed to exit boot services: {status:#x}"
quit()
# ======= NO MORE UEFI BOOT SERVICES =======
...
This time the call to exitBootServices should succeed, but we won't see a [success] message in the console. We'll know that it succeeded if no error messages are printed.
Great! We're done with the UEFI Boot Services. Now we're ready to jump to the kernel image. We'll do this in the next section.